A positive displacement flow meter is used to measure the flow rate of fluids. They operate by separating the flow into volume, counting sections, and multiplying each section by volume. It is a type of flow meter that operates without any need for external power or special mechanism. The gathering of its readings depends on the pressure from the upstream and downstream of the inlet and outlet ports. Read More…
Sierra manufacturers high performance mass flow meters and controllers for nearly any gas, liquid or steam. Customers choose Sierra when they need an accurate and repeatable flow measurement, short delivery lead times, expert flow advice and long term support. When it matters, choose Sierra. Visit www.sierrainstruments.com.
Aalborg Instruments & Controls is a globally recognized manufacturer of precision instrumentation for flow measurement and control. We offer variable area flow meters, thermal mass flow controllers, and more. Since our founding in 1972, it has been our commitment to develop, produce and deliver the highest quality products and services, as well as consistently meet or exceed customer...
Ryan Herco Flow Solutions is a leading national distributor for fluid handling products. Our family of products include; Flowmeters, sensors, instrumentation tubing and hose, process pipe and fittings, valves, pumps, filters and filter systems, storage and drums, and corrosion resistant structural products. We have 29 U.S. Service Centers ready to serve you.

Our flow meters are meticulously designed with you in mind. Our products have an unrivaled reputation, because we spend hundreds of engineering hours working on new and better ways to improve our products. No matter what you need, we can get if for you! Our staff is dedicated to helping you every step of the way. Contact us today for more info!
We are ONICON Incorporated, a leading manufacturer of flow meters and energy measurement systems. Our products and solutions are used in a wide range of applications, including HVAC, building automation, and industrial processes.
More Positive Displacement Flow Meter Manufacturers
How a Positive Displacement Flow Meter Works
For a positive displacement flow meter to provide accurate readings, its chamber has to be continually filled and emptied. The flow rate is calculated by the filling and emptying cycle. The measurement of the flow is created by the turning of the impeller inside the flow meter the rotation of which provides the meter readings.
Unlike other types of flow meters, a positive displacement flow meter provides accurate data regarding the volume of the fluids that pass through it. The center of the flow meter has a rotor that revolves on ball bearings that rotate the evenly placed blades of the impeller. As fluids enter the flow meter, the rotor and blades rotate around the cam, which causes the blades to move outward.
As the blades are turning, chambers form between the blades, rotor, base, covering, and housing. This movement is much like a revolving door. When the fluid passes through each of the chambers, it is counted to provide readings. This type of motion requires that the blades on the impeller and the surface of the casing to be tightly sealed to ensure accurate readings and prevent leakage.
Electronic pickup coils in the positive displacement generate pulses according to the volume of fluid passing through the meter. The ratio of the pulses per unit is the meter factor. Positive displacement meters are affected by the changes in the viscosity of the fluid.
Types of Positive Displacement Flow Meters
As with all forms of meters, no one positive displacement flow meter can be used for all types of fluid. The various types are chosen according to the fluid that is to be measured and the required accuracy of the data. The various types include rotary vane, helix flow, nutating disc, oval gear, lobed impeller, piston, and diaphragm.
A diaphragm type displacement meter has several diaphragms for the liquids to pass through. To keep the fluid moving through the meter, a rotating crank moves it smoothly along. This type of meter is used with gases.
A lobed positive displacement flow meter has two lobes in the chamber with one being an inlet and the other being outlet. The fluid is drawn in by one of the impeller lobes and pushed out by the other. The flow rate is measured by the number of revolutions of the rotors.
Unlike the other types of positive displacement flow meters, piston types have a piston in the center of the chamber. The piston blocks the outlet port of the chamber. As the fluid passes through the inlet port, it places pressure on the piston causing it to move up the chamber and down when the fluid exits.
Rotary vane flow meters have impellers with two or more compartments. As the impellers turn, the fluid is drawn in through the inlet causing the impellers to rotate. The flow rate is counted by the number of turns of the impellers.
A helix positive displacement flow meter has two helical rotors geared together with very little clearance between them in the casing. As the fluid flows in, the two rotors move the liquid axially from one end of the chamber to the other. This type of meter is used for high viscosity liquids.
Nutating disc meters have a movable disc instead of helixes or impellers that is mounted on a sphere. The displacement part of the meter is the disc with its lower part in contact with the bottom of the chamber and its upper part next to the top of the chamber. The liquid enters through the lower inlet side of the chamber and causes the sphere and disc to turn such that the liquid exits through the upper part of the chamber. The flow is measured by the rotations of the disc.
Oval gear meters have two rotors connected by gear teeth that seal the inlet and outlet flow. As the fluid enters, it turns the teeth of the gears, which turns the rotor. A fixed amount of fluid is allowed to enter with each turning of the gears. Much like the other positive displacement meters, the flow rate is measured by the turning of the shaft.






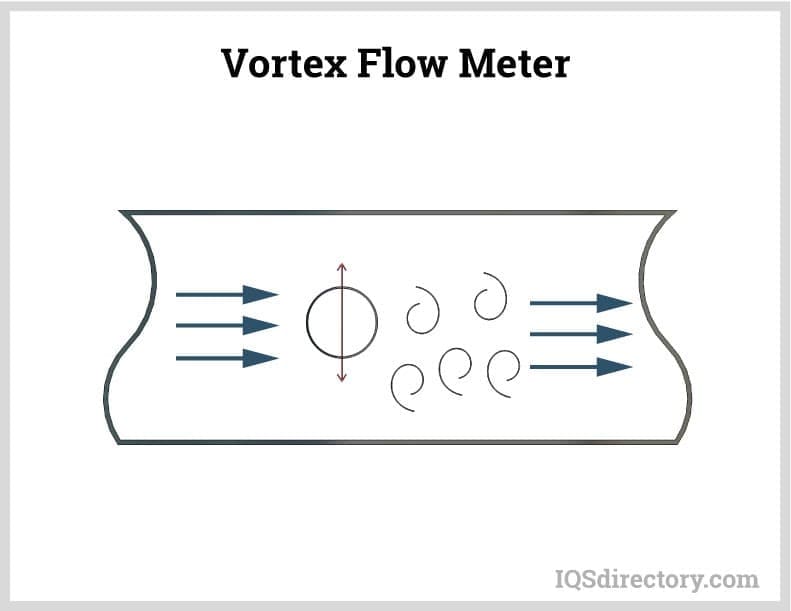
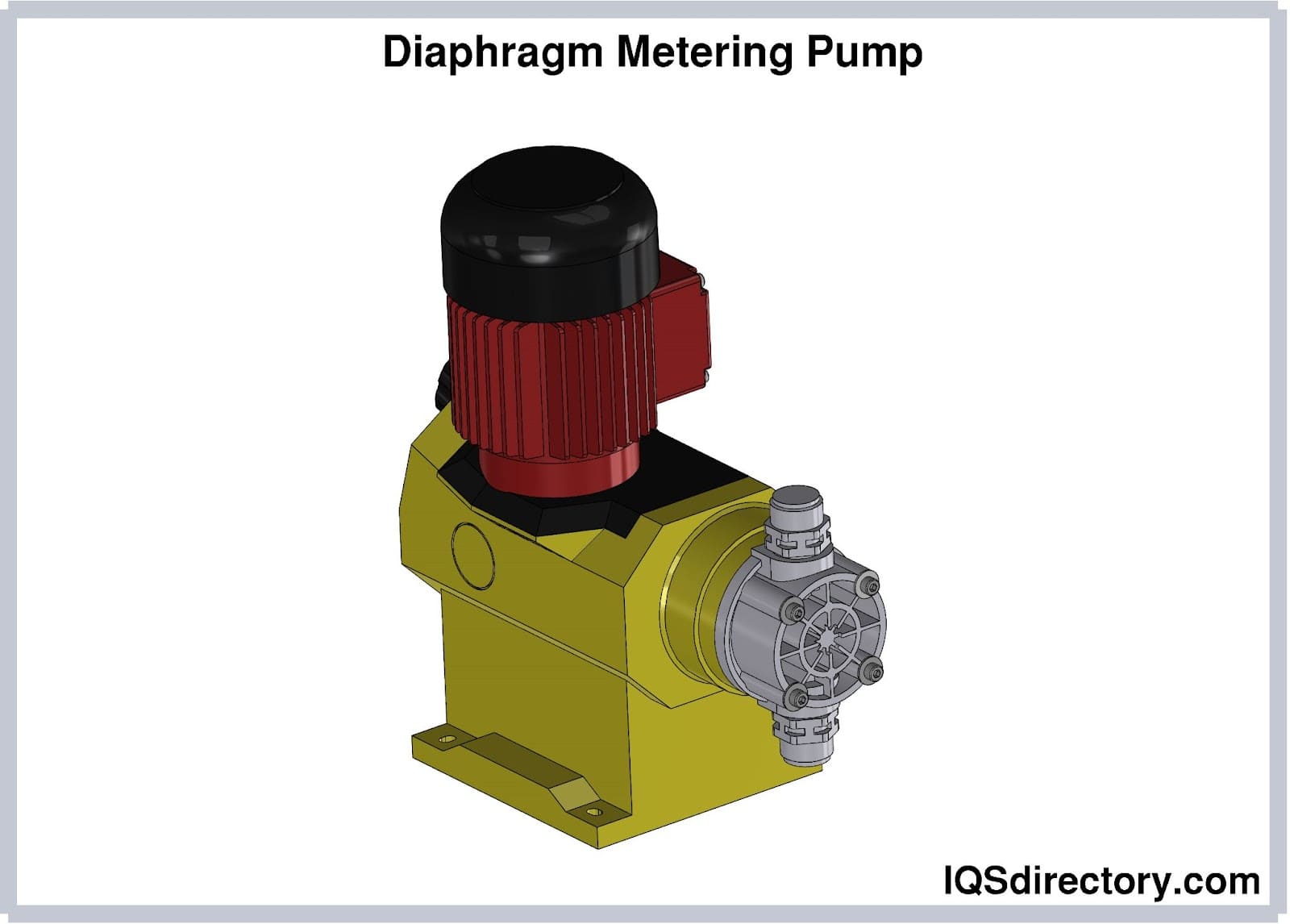

 Flow Gauges
Flow Gauges Flow Indicators
Flow Indicators Flow Meters
Flow Meters Flow Switches
Flow Switches Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services